Causes Reactive Hypoglycemia, Symptoms And Diet
7:30 PM | Posted by
Unknown |
Edit Post
Reactive hypoglycemia describes episodes of symptomatic hypoglycemia, and it takes 2-4 hours to occur after meals rich in carbohydrates. Read this article to know the causes, symptoms and diet reactive hypoglycemia.
Reactive hypoglycemia is also known as postprandial hypoglycemia. It is a medical term that describes cases of symptomatic, and it takes 2-4 hours to occur when you take a high-carbohydrate meal or an oral glucose load. He believes it is the result of excessive insulin release. The high carbohydrate meal is behind this phenomenal change. This process, which comes from the food passes through the digestive and elimination of glucose. Definitions of reactive hypoglycemia is controversial. The term reactive hypoglycemia Whipple meets criteria similar to the symptoms that can measure blood sugar low and high dose of glucose and soothes. The idiopathic postprandial syndrome are similar and no evidence of sugar in the blood is abnormally low.
Cause
Fifteen percent of people who have had abdominal surgery Alimentary hypoglycemia is a result of the dumping syndrome. The hormone is missing hormonal hypoglycemia hypothyroidism. Helicobacter pylori induced gastritis and the reason behind it is the bacteria that cause reactive hypoglycemia. End of occult hypoglycemia diabetes concerns, delaying the release of insulin by the B cells of the pancreas to the beginning. This results in an initial exaggeration of hyperglycemia during a glucose tolerance test. Idiopathic reactive hypoglycemia is a notion that is not existing, but because scientists know the causes of reactive hypoglycemia. A small blood glucose test or an outpatient carbohydrate is the current standard.
Therefore, hypoglycemia can occur as a side effect of some diabetes medications. This includes anti-insulin or oral diabetes. Pills to increase insulin production. They can be chlorpropamide (Diabinese), glimepiride (Amaryl), glipizide (Glucotrol, Glucotrol XL), glyburide (Diabeta, Glynase, Micronase), nateglinide (Starlix), repaglinide (Prandin), sitagliptin (Januvia) tolazamide and tolbutamide. A combination of pills to cause hypoglycemia, which include glipizide + metformin (Metaglip), glibenclamide + metformin (Glucovance), pioglitazone + glimepiride (Duetact), rosiglitazone + glimepiride (Avandaryl), and sitagliptin + metformin (Janumet).
Symptoms
Symptoms vary the volume and sensitivity of the speed or decreasing the size of individual blood sugar levels. The symptoms of hypoglycemia, caused by food can be a coma, heart palpitations or ventricular fibrillation, fatigue, dizziness, fainting, sweating, headache, depression, nervousness, irritability, tremor, flushing, sweet desire, increased appetite, nose Runny (rhinitis), epileptic-type response to rapidly flashing lights, nausea, vomiting, panic attacks, and numbness or coldness of the extremities.
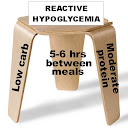
Reactive hypoglycemia diet
The breakfast menu sample can be half a cup of orange juice, cereals, third, fourth cup whole-wheat toast 1, c. 1 teaspoon margarine, 1 cup of skim milk and coffee, cream and sugar substitute. Release can be 2 oz lean hamburger, hamburger bun, salad or a slice of tomato, cup cooked carrots, salad, 1 cup tablespoons Italian dressing, apple, sugar, gelatin, and a cup of milk skim. Dinner can be 2 g of chicken breast cooked, half cooked medium potatoes, cup green beans, half cup of strawberries, a bagel, 1 c. teaspoon margarine and soft drinks. Breakfast can be a snack Med orange, the release includes a tea cup skim milk 3 graham crackers and snack dinner cranberry juice may be a third, a spoonful of peanut butter and crackers 6.
Pictures/SnapShot :



Reactive hypoglycemia is also known as postprandial hypoglycemia. It is a medical term that describes cases of symptomatic, and it takes 2-4 hours to occur when you take a high-carbohydrate meal or an oral glucose load. He believes it is the result of excessive insulin release. The high carbohydrate meal is behind this phenomenal change. This process, which comes from the food passes through the digestive and elimination of glucose. Definitions of reactive hypoglycemia is controversial. The term reactive hypoglycemia Whipple meets criteria similar to the symptoms that can measure blood sugar low and high dose of glucose and soothes. The idiopathic postprandial syndrome are similar and no evidence of sugar in the blood is abnormally low.
Cause
Fifteen percent of people who have had abdominal surgery Alimentary hypoglycemia is a result of the dumping syndrome. The hormone is missing hormonal hypoglycemia hypothyroidism. Helicobacter pylori induced gastritis and the reason behind it is the bacteria that cause reactive hypoglycemia. End of occult hypoglycemia diabetes concerns, delaying the release of insulin by the B cells of the pancreas to the beginning. This results in an initial exaggeration of hyperglycemia during a glucose tolerance test. Idiopathic reactive hypoglycemia is a notion that is not existing, but because scientists know the causes of reactive hypoglycemia. A small blood glucose test or an outpatient carbohydrate is the current standard.
Therefore, hypoglycemia can occur as a side effect of some diabetes medications. This includes anti-insulin or oral diabetes. Pills to increase insulin production. They can be chlorpropamide (Diabinese), glimepiride (Amaryl), glipizide (Glucotrol, Glucotrol XL), glyburide (Diabeta, Glynase, Micronase), nateglinide (Starlix), repaglinide (Prandin), sitagliptin (Januvia) tolazamide and tolbutamide. A combination of pills to cause hypoglycemia, which include glipizide + metformin (Metaglip), glibenclamide + metformin (Glucovance), pioglitazone + glimepiride (Duetact), rosiglitazone + glimepiride (Avandaryl), and sitagliptin + metformin (Janumet).
Symptoms
Symptoms vary the volume and sensitivity of the speed or decreasing the size of individual blood sugar levels. The symptoms of hypoglycemia, caused by food can be a coma, heart palpitations or ventricular fibrillation, fatigue, dizziness, fainting, sweating, headache, depression, nervousness, irritability, tremor, flushing, sweet desire, increased appetite, nose Runny (rhinitis), epileptic-type response to rapidly flashing lights, nausea, vomiting, panic attacks, and numbness or coldness of the extremities.
Reactive hypoglycemia diet
The breakfast menu sample can be half a cup of orange juice, cereals, third, fourth cup whole-wheat toast 1, c. 1 teaspoon margarine, 1 cup of skim milk and coffee, cream and sugar substitute. Release can be 2 oz lean hamburger, hamburger bun, salad or a slice of tomato, cup cooked carrots, salad, 1 cup tablespoons Italian dressing, apple, sugar, gelatin, and a cup of milk skim. Dinner can be 2 g of chicken breast cooked, half cooked medium potatoes, cup green beans, half cup of strawberries, a bagel, 1 c. teaspoon margarine and soft drinks. Breakfast can be a snack Med orange, the release includes a tea cup skim milk 3 graham crackers and snack dinner cranberry juice may be a third, a spoonful of peanut butter and crackers 6.
Pictures/SnapShot :






Related Articles from our archive : coffee,
diet
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
Category
- coffee (260)
- coffee blend (4)
- coffee mixed (2)
- coffee recipes (1)
- coffee type (2)
- diet (168)
- health (171)
- weight loss (108)










0 comments:
Post a Comment